Animal Health TIMPs
Introduction
Animal health management deals with monitoring the health status of the animals on the farm. It is apparent that a healthy animal will be productive while unhealthy animal apart from not been productive becomes a liability as money would be spent for their treatment. Managing animal health involves the prevention, control and if possible eradication of animal diseases


- Confers life-long protection against ECF
- Used in combination with 30% oxytetracycline antibiotic to prevent parasites from causing clinical disease.
- Administered by trained personnel
- Animals immunized with this vaccine require minimal tick control.
- East Coast Fever (ECF) Vaccine will prevent occurrence of ECF
- Consult a veterinary
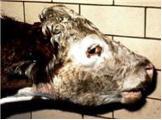
A cow with respiratory distress
- Contagious Bovine Pleuropneumonia is a transboundary disease that lowers productivity and restricts trade along the beef value chain in Kenya.
- Contagious bovine pleuropneumonia (CBPP) Diva vaccine will prevent occurrence of CBPP

Herd of Orma boran
- An indigenous cattle breed with ability to survive and remain productive in high tsetse challenge zones with minimal curative and prophylactic treatments against nagana.
- Adapted to the semi-arid and arid areas particularly in Tana River County
Medicated MUMB is a composite feed supplement made from molasses, urea and mineral premixes infused with a dewormer for the control of chronic worm infections especially in lactating cattle, calves, sheep and goats.
Feeds in the ASALs are of low quality and chronic worm infections are quite prevalent in these areas. MUMBs are a cheap alternative to commercial supplements and are a source of nitrogen and energy during drought.

MMUMB block

Goat licking MMUMB bloc
Biosecurity measures on the farm and along the indigenous chicken houses, including slaughter facilities, and those hatching own eggs, so as to improve productivity of indigenous chicken and reduce the risk of zoonotic diseases,

Foot and vehicle bath at the entry of a poultry unit