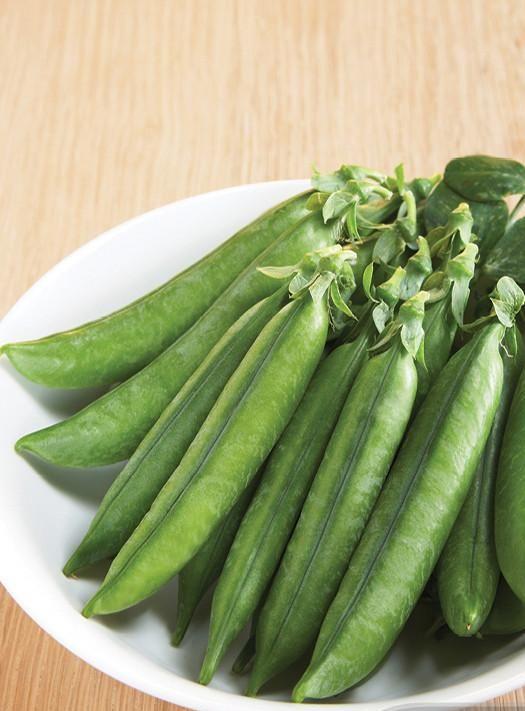
Garden Peas
Garden Pea (Pisum sativum). Common names: Garden pea, Shelling pea, English pea, Green pea, Minji, Sweet pea
Pea is a green, pod-shaped vegetable, widely grown as a cool-season vegetable crop. There are generally three types of peas that are commonly eaten: garden or green peas, snow peas and snap peas. Garden peas have rounded pods that are usually slightly curved in shape with a smooth texture and vibrant green colour. Inside of them are green, rounded pea seeds that are sweet and starchy in taste. Snow peas are even and thinner than garden peas and are not dense.
Snap peas, obtained by crossing garden and snow pea, and are characterized by fleshy shells with a crunchy, brittle texture. The shells of both snow peas and snap peas are edible, and both feature a slightly sweeter and cooler taste than the garden pea. Garden peas are cultivated for fresh green seeds, tender green pods, dried seeds and foliage. Garden peas are a major commercial crop as a vegetable where large amounts are canned while dried seeds may be used as feed or ground to flour and consumed as food. Varieties grown for their tender pods for export market include snap peas/sugar snaps and snow/ sweet peas

|
Photo of Variety |
Description |
|
|
Variety name: Green feast.
|
|
|
Variety name: Alderman.
|
|
|
Variety name: Summerwood
|
|
Source: yates.com.au |
Variety name: Dwarf Earlicrop
|
|
|
Variety name: Ambassador
|
- Choose a site that is well draining.
- Preferable soil PH 5.5 -6.8. Install poles or trellis because peas are supported by the poles to grow well.
Climatic requirements and soils
- Altitude: above 1800mas; 1500 to 2600 meters above sea levels.
- Temperature: 12 to 20oC.
- Rainfall: 1500 to 2100mm.
- Soils: sandy loams to clay loams.
- Plough the land and harrow to fine tilth.
- At this point, add 1000kg of manure per acre to improve soil structure and soil fertility.
- Intercropping of garden pea can be done with maize, grasses or other crops.

Poorly prepared land

Well prepared land
Based on soil test results. An indicative recommendation on light medium-rich alkaline soils is 40 kg N, 50 kg P, 150 kg K and 30 kg Mg per hectare for optimal yields (DAFF, 2011). For higher yields K application can be added up to 250kg/ha.
- Seed rate – 70 to75kg/ha (28 to 30kg/acre).
- Put in place trellises to help support the garden pea crop.
- Plant 5 to 7cm apart in double rows supported by trellis. Space rows 45 to 60 cm apart for single or pairs of rows and 20 -25cm between the pairs.
- Soaking seeds before planting is helpful.
- Plant evenly about 20 or 30 peas per metre of row in single or double lines.

Well established garden pea crop (Source: https://www.fwi.co.uk/)

Trellising Garden pea (Source: alamy.com)
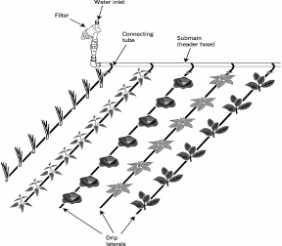
- Garden pea requires moist conditions to be maintained consistently.
- When soil is dry, apply water which you have harvested from rain by irrigation, mostly by drip irrigation.
- Drip irrigation saves up to 70% of the water.
- When the crop is still young, remove weeds to reduce competition for water, nutrients and space.
- Reduce chances of disease developing because of moist conditions created by weeds.
- Control weeds by manual weeding, cultural methods like mulching, mechanized weed control or use of herbicides.


- Garden peas are nitrogen fixing plants. Recommendation is to treat with Rhizobium culture which will enhance fixation of nitrogen nutrient.
- Minimal application of fertilizer is recommended from soil test results.
- Thinning is done to one plant per hill spaced 10cm apart.
- Training is done when the new crop has emerged since the support is put in place before planting.
- The plant is held gently and attached on the trellises for support.





