Cotton TIMPs
Introduction:
Cotton is the most important fibre crop in arid and semi-arid regions of Kenya. It is used in making clothes and in the manufacture of cooking oil and cottonseed cake for animal feed.
KSA81M
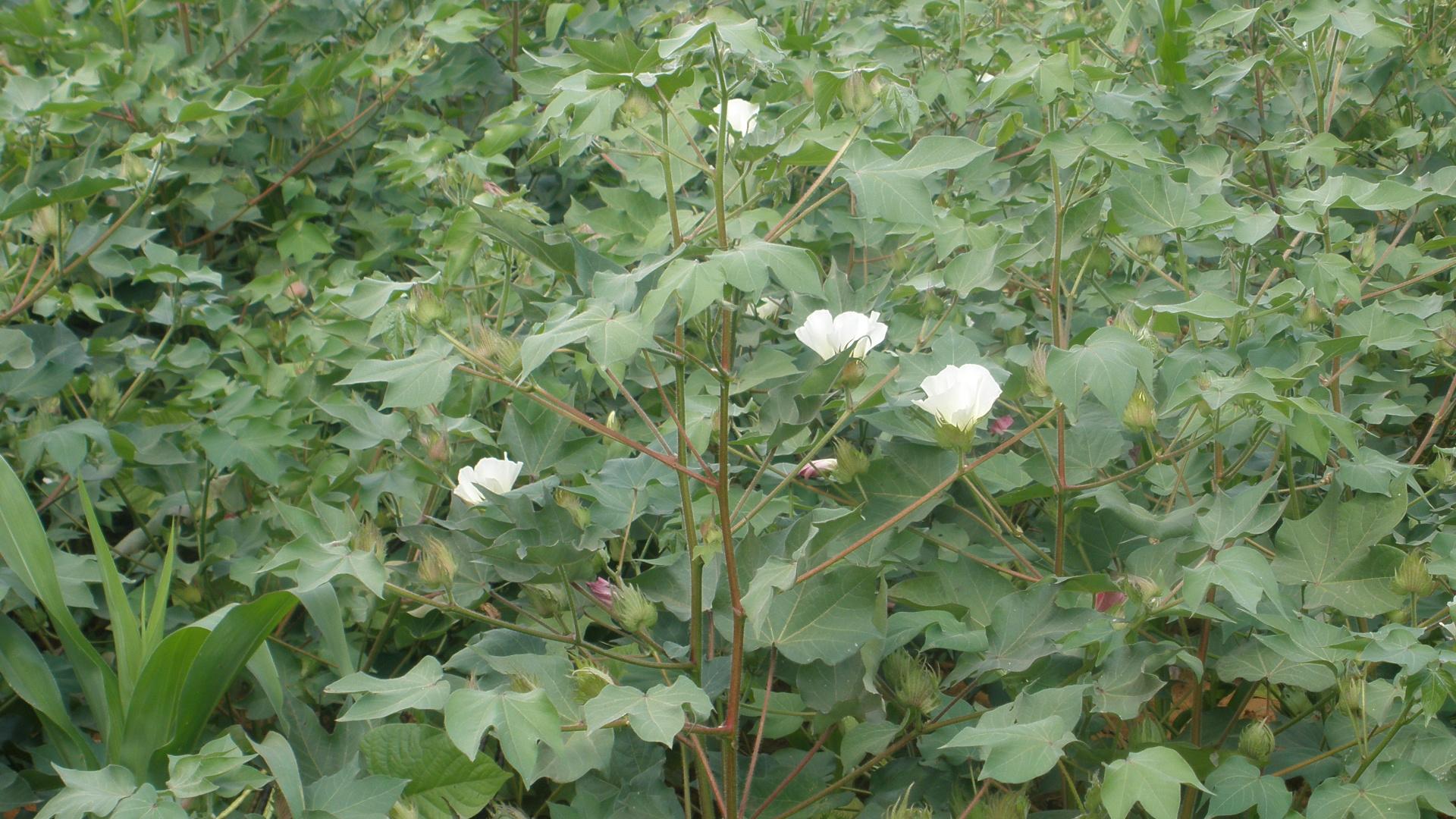

- KSA81M self-pollinated variety, medium maturing and moderate yields (2000kg/ha) and 38% gin outturn.
- Grow well in Nyanza, western and Rift valley areas.
- Matures in 180 days in western Kenya region
- Fairly resistant to verticillium wilts and jassids.
HART 89M


- HART89M is self-pollinated variety.
- It is a drought, heat tolerant and long maturing having ability to regrow after dry season.
- Grows well in coastal and semi-arid lowlands east of rift valley.
- Matures in 300 days in Eastern and Central regions and 150 days at Coast.
- Potential seed yield is 1200kg/acre or 3000kg/ha.
- Under irrigation the yield is increased by 36-40%.
- Resistant to bacterial wilts and jassids.
AMIRAN HYBRIDS HA701
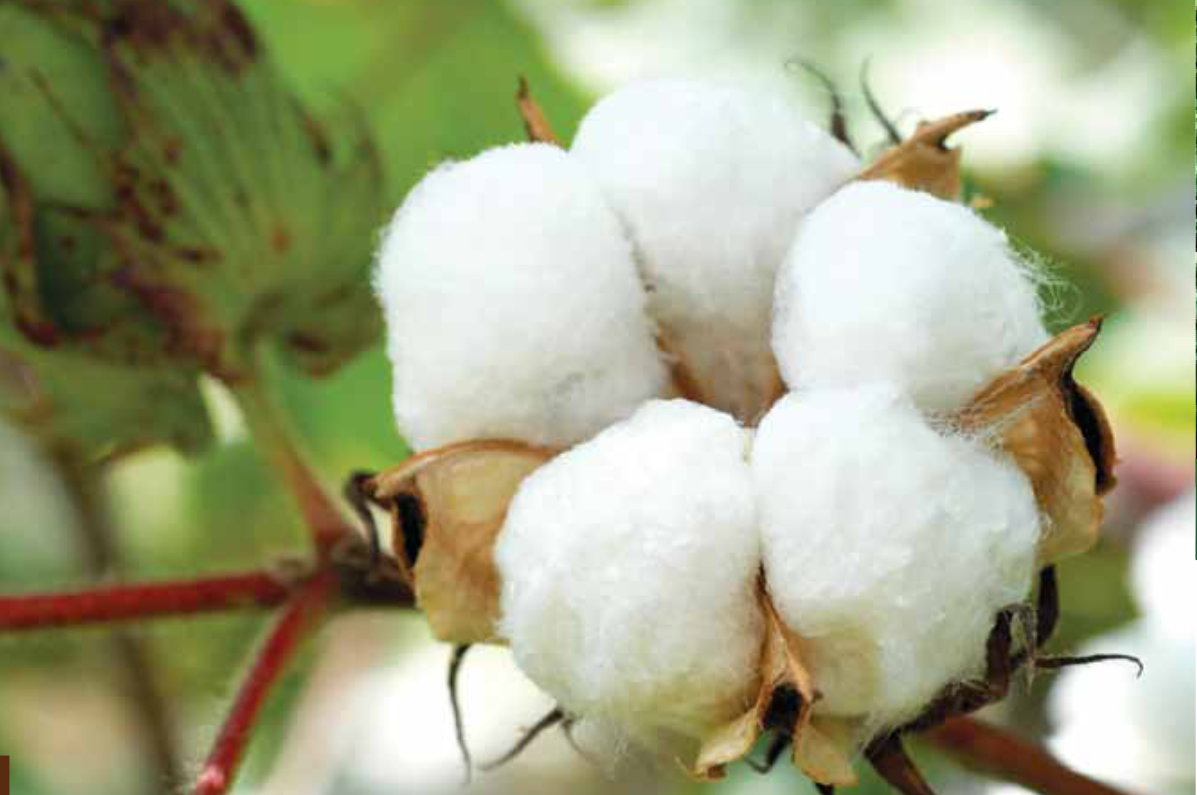

- The variety is medium maturing.
- Moderate yields (2000kg/ha).
Cotton Variety (MAHYCO Bt.)

Bt Cotton Variety MAHYCO
Source :https://infonet-biovision.org
- The cotton varieties with Bt. gene have tolerance to boll worms.
- Potential yield 4000kg/ha.
- Choose an area with well drained clay, sandy loam soils.
- Soil PH 5-8.5.
- Altitude: 0-1500 meters above sea level.
- Temperature: 20 to 27oC.
- Rainfall: 250 to 1200mm.

Land Preparation
- First clear the bush.
- Plough with tractor, animal drawn or hired labour.
- Harrow the field.
Planting
Pure Stand
- Recommended spacing is 100X30 cm.
- Plant 1-2 seeds of de-linted cotton seed or 3-5 fuzzy seed at 2.5cm deep per hill.
- Use 7 kg of fuzzy seed per acre (17.5 kg ha–1) instead of only 3 kg per acre or 8 kg ha–1 for de-linted seed.
- Do gapping after 2 weeks of growth.
- Thin to one plant per hill after 3 weeks.
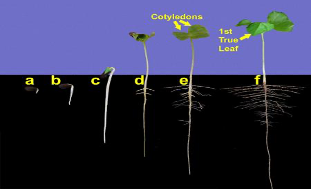
Stages of cotton germination

Cotton seedling
Intercropping of Cotton with Legumes
- Plant two rows of legumes such as beans between two rows of cotton plant.
- Spacing for cotton 100 X 30cm
- Intercrop 25cm from cotton rows with bean spacing at 50 by 10 cm during first crop.
- During the second season no crop can be planted because cotton have formed big canopy.
- Strip cropping one row of pigeon peas after every 5 rows of cotton plants.
- Spacing for pigeon peas is 550 cm X 50cm in strip cropping systems.
- Intercropping and strip cropping increases the returns by 50 to 60% percent.
Thinning
- Thin after 3 week of plant growth to one plant per hill in pure stand or intercropping systems.
- Failure to thin when it is necessary reduces seedcotton yields due to competition for soil nutrients, light and water while failure to gap when necessary results to poor crop stand and low yields.

Thinning and gapping
Water Management
- Plant before the onset of rainfall.
- Irrigate during boll formation if rainfall fails.
- To conserve water use fanya Juu Terraces and water retention ditches.
- Making furrows parallel to the contours ensures that rainfall and runoff are spread evenly over a field.
- Zai Pits are small planting holes measuring 15-30 cm in width, 10-20 cm deep and spaced 60-80 cm.
- They harvest and stores water for prolonged crop use.
- Plant seeds into the holes after filling one to three handfuls of organic material such as manure, compost, or dry plant biomass.
Soil Fertility
- Use soil results to guide you on the fertilizer to use.
- Apply triple Superphosphate (TSP) or Diamonium Phosphate (DAP) during planting at 135 kg/ha.
- Top dress with Calcium Ammonium Nitrate (CAN) or Sulphate of Ammonia (SA) at 100 kg/ha or half this quantity of Urea.
- Sulphate of Ammonia and Urea have some acidifying effects and is generally used in coast province.
- Apply manure at a rate of 2 to 4 tons per acre depending on soil test results and recommendation.
- Use of growth hormone enhance plant growth and yield.
- Recommended rate: 2% zinc foliar +25 ppm growth enhancer or 2% zinc foliar+ 50 ppm growth enhancer as a foliar spray when cotton plants are at 4-5 leaf stage.
Method:
∙ Apply 50 kg DAP fertilizer at planting.
∙ Mix growth enhancer to water in the ration of 1:2 (use 10 litres of the mixture in water for one acre).
∙ Add 960 g of 2% zinc mineral.
∙ Apply when the cotton is at 4-5th leaf stage as top- dress.
∙ Also apply CAN (50kg per acre).
- This increases and doubles the profit.
Symptoms of nutrient deficiency
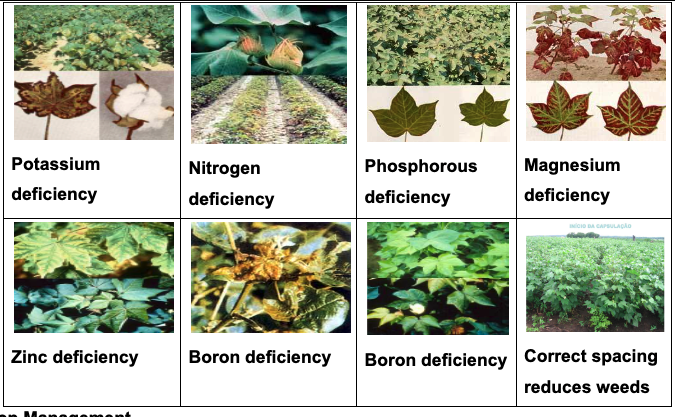

Crop Management
- Use the recommended spacing for cotton.
- Apply fertilizer when needed.
- Use appropriate weed and pest control methods
Weed Management
- Weeds causes cotton yield losses between 60 – 90% of the potential yield.
- Weed 3 weeks after crop growth and thereafter depending on weed densities.
- Do crop rotation.
- Do intercropping.
- Use pre-plant herbicide.
- Do mechanical or manual hand weeding to remove weeds that escaped herbicide and put mulch.
- Mulching cotton field will control weeds and conserve water.
Common cotton weeds

Chickweed

Wild lettuce

Cleavers

Mexican marigold

Black jack

Gallant soldier

Goat weed

Wandering jew
Mulching
- Put mulch between cotton plants three weeks after crop growth.
Chemical Control
- Use selective herbicides registered for use in cotton field.
Mechanical Weeding


- Use draft animals motorized weeding to supplement manual labour.
- Post sowing treatments (Use of herbicides)
- Using pre-emergent herbicides and selective post emergence herbicides.
- When doing manual weeding use pangas and jembes.
Fusarium wilts

Source: TexasAgrilife Extensionhttps://agfax.com/2018/09/12/texas-cotton-new-race-of-fusarium-wilt-how-to-limit-spreading/
- Occurs at seedling stage and peaks at flowering stage.
Damage Symptoms
- Yellowing and necrosis of lower leaf margins.
- The vascular system of infected plants become discolored.
Management.
- Use adequate seed rate.
- Do not plant deeper than 2.5 cm.
- Rotate cotton with sorghum and small grains
- Always use seed treated with appropriate fungicides and insecticide mixtures.
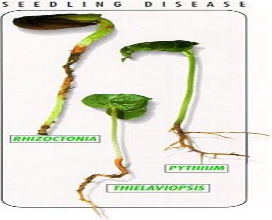
Cotton seedlings diseases Source: Munro, J.H. 1987
- They are caused by fungus Pythium and Rizoctonia species that causes mortality during germination.
Damage symptoms
- Rotting of roots.
- Death of seedlings.
Management
- Use approved seed.
- Practice field sanitation.
- Rotate cotton with maize, wheat, barley, sorghum, safflower or rice.
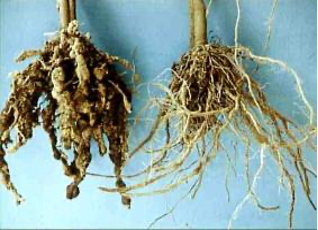
Root knot nematode
Source: https://infonet-biovision.org
Damage Symptoms
- Wilting of cotton plants.
- Roots have galls.
- Drying of plants.
Management.
- Use recommended nematicide (PCPB).
- Crop rotation is a cost effective means.
- Rotate cotton crops such as maize, peanut and soybean grain sorghum, rice and tobacco .

Damping off (Rhizoctonia spp)
- It can cause significant yield reduction.
Management
- Effective control:
- Crop rotation,
- Field hygiene,
- Use of clean seed, not planting cotton in a Rhizoctonia spp, Pythium, Fusarium spp. complex infected field.
- Applying biocontrols (Trichoderma fungi) in the soil.
Control Practices.
- Check for pests and diseases after plant growth
- Biological control – introduction of natural enemies, by using need based insecticides.
- Use of resistant variety.
- Seed dressing -Cotton seeds are coated with insecticide/fungicide to protect seedlings from early pests and diseases.
- Chemical control - Farmers can use the recommended pesticides from the list by PCPB.
- This assist in management of early seedling pests and diseases.
- Use resistant variety.
- Use approved seed.
- Treat seed with a fungicide or heat to destroy the fungus on the seed and to protect the emerging seedlings from infection.
- Apply recommended fungicide (PCPB list which is updated yearly).
- Cotton matures 150 days to 300 days after planting depending on cotton growing zones.
- Harvest as soon as boll are open.
- Harvest as soon the cotton boll splits open.
- Use two bags, one for AR grade (non- stained cotton) and BR (stained cotton) when picking cotton in the field.
- Use sisal bags or jute bags or cotton bags.
- After the last picking, all cotton stalks should be uprooted or chopped off below ground, collected into heaps left to dry and then buried in the soil.
- At ginnery, separate between the lint (white fluffy part) and cotton seed.


- Store in well ventilated store.
- Proper storage management practice for seed cotton, lint and
cotton seeds preserve their quality and quantity. - This is achieved by storing different grades for each material category separately to avoid mixing.

- Sort the grades for AR grade (non- stained cotton) and BR (stained cotton) when picking cotton in the field separately.
- Drying of seed cotton reduces moisture content which help reduce on loss of quality and quantity during storage.
- It is achieved by drying seed cotton to safe storage moisture content of
11% in rodent proofed setting immediately after harvesting in a secure, dry, clean, aerated tidy environment. - Such systems include well designed raised platforms.
- Different seed cotton grades are dried separately to maintain integrity of the grades.

- Cotton lint is used weaving.
- Cotton seed is used to extract cooking oil
- Cotton seed cake is used for animal feed.
Cottonseed cake Screw-press
Power tiller
A Power Tiller can be used in seedbed preparation, sowing seed, planting seed, spraying fertilizer,
herbicide and even irrigation.
Wheeled tractor
- Can be used in seedbed preparation, sowing seed, planting seed, spraying fertilizer, herbicide and even irrigation. In addition, it can also be used for threshing through a power take off device and transporting produce.
- A ridger is a device drawn by a tractor used in agriculture that gathers and heaps up the loose soil for planting.
- Cotton planter is a device used in agriculture that opens furrows meters, sows seeds for Cotton by positioning them in the soil and burying them to a specific depth and forms a ridge along the seed row.
- The Cotton planter sows seeds at the proper seeding rate and depth, ensuring that the seeds are covered by soil.
Cotton weeder
weeds in a cotton plantation. It works by lifting the soil from the bed between the rows using two opposed mouldboards and pushing it to the root zone of the plants. Weeds are buried in the soil by the weeder shares
- Basic cost KES 15,000 per acre.
- Estimated returns KES 28,800 per acre. Returns =KES 13,800.
- Internet/online/mobile marketing e.g Kamis and Nafis National Agricultural Commodities Market Information (NAFIS) http://www.nafis.go.ke/category/market-info/.
- Contract farming with Ginneries.
- Farmers to form cooperatives to help in negotiation of prices with Ginneries.
Cotton Production Handbook, A guide for farmers and extension. CODA 2013
D. R. Karanja, C.M. Githunguri, L. M’Ragwa, D. Mulwa and S. Mwiti (2006) Variety, Characteristics and Production Guidelines of Traditional Food Crops. KARI Katumani Research Centre
Munro, J.H. 1987. Cotton. Tropical Agricultural Series. Longman Group UK Limited. 436p
PCPB 2020. List of recommended pesticides for use in Agriculture.
Recommendations for growing cotton in Kenya. Second edition 2006
Tanzanian cotton growing hand book, 1968
Kathuli, P., Kisilu R., Karanja D.R., Mweki, R. and A.O. Adongo. 2017. Growth Enhancers Increase Yield and Profitability of Gadam Cotton in ASALs. ebsite:www.kalro.org/asal-aprp
Contour bund extension manual and leaflets KALRO Extension Brochure, Kabete
Extension manual and leaflets on Zai Pits in cotton farming
Kathuli, P. & Itabari, J. K. (2015). In situ soil moisture conservation: Utilization and management of rainwater for crop production. In: Adapting African Agriculture to Climate Change. Springer, Cham, Switzerland, pp. 127–142. Mati, B. M. (2005). Overview of water and soil nutrient management under smallholder rain-fed agriculture in East Africa. Working Paper 105. International Water Management Institute (IWMI), Colombo, Sri Lanka
Contacts
Kenya Agricultural and Livestock Research Organization
P.O. Box 57811-00200, Nairobi, Kenya
Call: 011101010